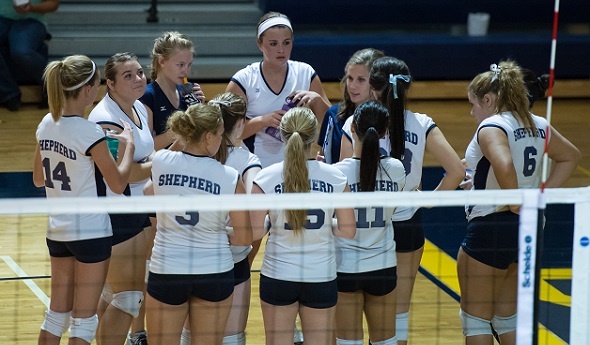
Using Heads in the Heat of Competition
December 20, 2013
By Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
With so much recent attention to the risks and recognition of concussions in collision sports, athletic leaders have put their heads together to address far more common – but often overlooked – threats to the health of our student-athletes: heat and sudden cardiac arrest.
The No. 1 killer of young athletes is sudden cardiac arrest, while heat stroke victims can surpass that during the year’s hottest months. While the moment of impact leading to a concussion is totally unpredictable, athletic trainers, coaches and administrators have the ability to diminish the occurrences of cardiac arrest and heatstroke. Typically, there is a pre-existing condition, or family history suggesting probabilities for sudden cardiac arrest, which can be treated when detected. And, the perils associated with hot weather – heat stroke, prostration – are almost always completely preventable.
The MHSAA has addressed both issues recently. With assistance from numerous medical governing bodies, the annual pre-participation physical form was revamped and expanded prior to the 2011-12 school year to include comprehensive information regarding participants’ medical history.
In May, the Representative Council adopted a Model Policy for Managing Heat & Humidity (see below), a plan many schools have since adopted at the local level. The plan directs schools to monitor the heat index at an activity site once the air temperature reaches 80 degrees and provides recommendations when the heat index reaches certain levels, including ceasing activities when it rises above 104 degrees.
The topic of heat-related illnesses receives a lot of attention at the start of fall when deaths at the professional, collegiate and interscholastic levels of sport occur, especially since they are preventable in most cases with the proper precautions. In football, data from the National Federation of State High School Associations shows 41 high school players died from heat stroke between 1995 and 2012.
“We know now more than we ever have about when the risk is high and who is most at risk, and we’re now able to communicate that information better than ever before to administrators, coaches, athletes and parents," said Jack Roberts, executive director of the MHSAA. “Heat stroke is almost always preventable, and we encourage everyone to avail themselves of the information on our website.
“Schools need to be vigilant about providing water during practices, making sure that students are partaking of water and educating their teams about the need for good hydration practices.”
All of which is not to say concussions aren’t a serious matter; they are. In fact, leaders in sport safety can take advantage of the concussion spotlight to illuminate these additional health threats.
A recent New York Times story (May 2013) by Bill Pennington featured a February 2013 gathering in Washington organized by the National Athletic Trainers Association. In the article, Dr. Douglas J. Casa, professor of kinesiology at the University of Connecticut and Chief Operating Officer of the Korey Stringer Institute (founded in the late NFL offensive lineman’s name to promote prevention of sudden death in sport), suggests just that.
“All the talk about head injuries can be a gateway for telling people about the other things they need to know about, like cardiac events and heat illness,” said Casa in the article. “It doesn’t really matter how we get through to people as long as we continue to make sports safer.”
Education and prevention methods need to find a permanent place in school programs if those programs are to thrive and avoid becoming targets at which special interest groups can aim budgetary arrows.
Dr. Jonathan Drezner, the president of the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, said in the New York Times piece that sudden cardiac arrest is “so incredibly tragic and stunning that people aren’t comfortable putting it into the everyday conversation. I do wish, to some extent, it was something people talked more about because we are getting to a place where we could prevent many of these deaths.”
When it comes to heat-related deaths or illnesses, the prevention efforts can be even more successful by educating the masses. And, these efforts can be done at minimal cost to schools.
“That’s the thing about curtailing exertional heat illness: it’s 100 percent preventable, and unlike other health threats to athletes, the solutions can be very low-tech and inexpensive,” said Dr. Michael F. Bergeron, the director of the National Institute for Athletic Health & Performance at the University of South Dakota’s Sanford Medical Center, in the New York Times story.
To assist with cost and data maintenance, the MHSAA has teamed with Sports Health to provide schools with psychrometers (heat measurement instruments) at a discounted rate, and has built online tools to track heat and humidity conditions.
Managing heat and humidity policy
- Thirty minutes prior to the start of an activity, and again 60 minutes after the start of that activity, take temperature and humidity readings at the site of the activity. Using a digital sling psychrometer is recommended. Record the readings in writing and maintain the information in files of school administration. Each school is to designate whose duties these are: generally the athletic director, head coach or certified athletic trainer.
- Factor the temperature and humidity into a Heat Index Calculator and Chart to determine the Heat Index. If a digital sling psychrometer is being used, the calculation is automatic.
If the Heat Index is below 95 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Optional water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
If the Heat Index is 95 degrees to 99 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Optional water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
Contact sports and activities with additional equipment:
- Helmets and other possible equipment removed while not involved in contact.
- Reduce time of outside activity. Consider postponing practice to later in the day.
- Recheck temperature and humidity every 30 minutes to monitor for increased Heat Index.
If the Heat Index is above 99 degrees to 104 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Mandatory water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
- Alter uniform by removing items if possible.
- Allow for changes to dry T-shirts and shorts.
- Reduce time of outside activity as well as indoor activity if air conditioning is unavailable.
- Postpone practice to later in the day.
Contact sports and activities with additional equipment
- Helmets and other possible equipment removed if not involved in contact or necessary for safety.
- If necessary for safety, suspend activity.
Recheck temperature and humidity every 30 minutes to monitor for increased Heat Index.
If the Heat Index is above 104 degrees:
All sports
- Stop all outside activity in practice and/or play, and stop all inside activity if air conditioning is unavailable.
Note: When the temperature is below 80 degrees there is no combination of heat and humidity that will result in need to curtail activity.
PHOTO: The Shepherd volleyball team includes hydration during a timeout in a match this fall.

MHSA(Q&)A: Stevensville-Lakeshore wrestling coach Bruce Bittenbender
February 9, 2012
Bruce Bittenbender grew up in Bethlehem, Pa., in the heart of steel country, and worked part-time in a mill as a young adult. That helped land him in Michigan City, Ind., not long after graduating from Milligan College in Tennessee in 1969.
But Bittenbender wanted to teach and coach.
Bittenbender took a teaching job at South Haven that fall, and as an assistant coach helped that school's wrestling team to the MHSAA Class B championship. A year later the wrestling coaching job opened at Stevensville Lakeshore. He says now that he was too young for the job, but Bittenbender applied and was hired. The program was struggling at that point -- but not for much longer.
According to the National Federation of State High School Associations' record book, Bittenbender trailed only Rex Peckinpaugh of New Castle, Ind., in career dual coaching wins heading into this season (796-780). Bittenbender won his 800th match on Jan. 14 -- and has his team just two more victories from MHSAA Finals weekend Feb. 24-25 in Battle Creek.
Bittenbender retired from teaching two years ago after 35 teaching biology and seven more physical education. At 64, he still gets on the mat with his wrestlers from time to time, although perhaps not as much as he once did. But countless wrestlers -- including those who won a combined 20 individual championships -- have benefited from his instruction.
His coaching tree includes current Rockford coach Brian Richardson and former Lowell coach Dave Strejc, who led teams to MHSAA Division 2 championships in 2002 and 2004. Bittenbender was named National Coach of the Year by the National Federation of State High School Associations in 2002 and again by the National High School Athletic Coaches Association in 2010. He is a member of the Michigan Wrestling Association Hall of Fame, and he will be inducted into the Pennsylvania Wrestling Coaches Association Hall of Fame this spring.
Stevensville Lakeshore is ranked No. 7 in Division 2. His team won its District on Tuesday, downing St. Joseph 35-34 with a decision win in the final match.
What keeps you coming back for another season?
Every year, when you think you've seen it all, something else comes up. When I was in middle school, it was junior high school back then, I was on the edge. The coach (Jim McIntyre, who went on to coach at Kutztown University) grabbed me on the back of the neck and said, "What are you doing?" I was hanging out with kids of questionable character, and he said, "You need to come out for wrestling." I still go back and play golf with that guy once in a while. ... I came from a big family. We didn't have much. I have empathy for the kids that were kicked around, misdirected. Somebody took time out for me. I felt maybe I could kick some of that back.
After so many wins, do you still enjoy all of them the same?
I tell ya, last night I certainly enjoyed the win. It was just like I was 23 again. Yeah, I enjoy it. It's addictive. That's what you're out there for.
The NFHS changed its wrestling weight classes this season, but Michigan chose to stay with its current lineup. What is your thought on that switch?
I think it's going to switch back. It makes no sense to me. The average kid graduating from high school is 5-(foot-)9, 155 pounds. Why add a weight class at the top where you have to compete for kids with football and basketball. … Our sport has prided itself on giving the little guy a chance. ... He can be a state champ in wrestling.
Your teams have finished MHSAA Finals runner-up twice. How much would you like to win that first championship?
I would love to. That's the ultimate goal. We've been so close. We were up three points in '94, and got pinned at heavyweight (to lose 28-25 to Fowlerville). In '86 we broke the record for individual number of points scored, but Eaton Rapids broke it too. We were that close.
I'm assuming you're not going to stop coaching any time soon.
Being around people and the community, and working with kids, it keeps you young. Keeps you in shape, keeps you motivated. I think that's one of the reasons. Now that I'm not teaching, my wife and I are able to travel quite a bit in the fall and summer. I think that's basically a motivator, just being around people.
What do you tell, or would you tell, young coaches who are just getting started in high school wrestling?
I tell them to be careful the first few years. It's different today. … I tell coaches you need to set up standards, discipline, goals and objectives, and go by those. You try to accommodate some of these kids, and this and that, but you can go only so far. You’ve gotta stick to the rules and let the cards fall where they are. If you don't, you'll have problems down the line.
And I think communicating with people, making friends, getting out there and strumming up support for the program is important too. I've had the opportunity to speak to the Lions Club, various civic organizations, at hospitals. You have to try to make yourself available. People have to learn to put their trust in you."

