Snap, Crackle & Pop: Why Do My Knees Make Noises - And Should I See a Doctor?
April 5, 2022
Do you ever just go about your daily life and then, seemingly out of nowhere, your knee makes a noise?
You might call it a weird idiosyncrasy and not think twice about it—or you might turn to the Internet to try and find all of the potential issues that might be wrong with your knee.
But if your knee pops or cracks once in a while, it’s usually no cause for concern. After all, joints sometimes make noises, and knees are no exception (especially when you squat or sit down.)
“Infrequent knee pops and cracks are more common in the younger population, says Nancy White, M.D., a sports medicine physician at Henry Ford Health. “When you feel that ‘pop,’ it means your kneecap was pulled a bit outside of where it’s supposed to be, and so it’s correcting itself and getting back into position. You can kind of feel that something moved.”
If, however, pain or swelling accompanies a noisy knee, you should have it evaluated by a sports medicine provider. And if your knee is popping or cracking regularly, that's another sign you should have it checked out.
“If you let it go, your knee could get worse,” says Dr. White. “There are recommendations a doctor can make to prevent this from happening, such as strengthening and flexibility exercises.”
What Is Knee Crepitus?
If your knee sounds like Rice Krispies crackling (or you experience a grinding sensation) it likely means you have knee crepitus, which can signify the beginning of osteoarthritis behind the kneecap.
“Knee crepitus is primarily caused by an issue called patellofemoral dysfunction,” says Dr. White. That sounds like a mouthful, but it means that your knee isn’t tracking straight up and down like it’s supposed to.
“There’s cartilage on the back of your kneecap and on the front part of your thigh, and the cartilage on the front part of your thighbone makes a groove so the kneecap can glide straight up and down in a floating position,” says Dr. White. “If the cartilage is worn down (and inflamed, worn-down cartilage signifies osteoarthritis), the kneecap can’t smoothly glide up and down, causing knee crepitus.”
If you are experiencing knee crepitus, you should see a sports medicine primary care physician, especially if it is accompanied by pain. They can recommend a variety of treatments, such as physical therapy and cortisone injections.
Still not sure if your noisy knees are cause for concern? When in doubt, call your doctor. After all, the sooner your doctor can examine it, the sooner you can prevent an issue from getting worse.
To learn more about your orthopedic condition or to find a provider, visit henryford.com/ortho.
Dr. Nancy White is a sports medicine physician with Henry Ford Health. She sees patients at Henry Ford Medical Center – Novi, and Henry Ford Medical Center – Bloomfield Township.
Fuel Up for Daytime Fasting with Proper Nutrition, Hydration
February 17, 2026
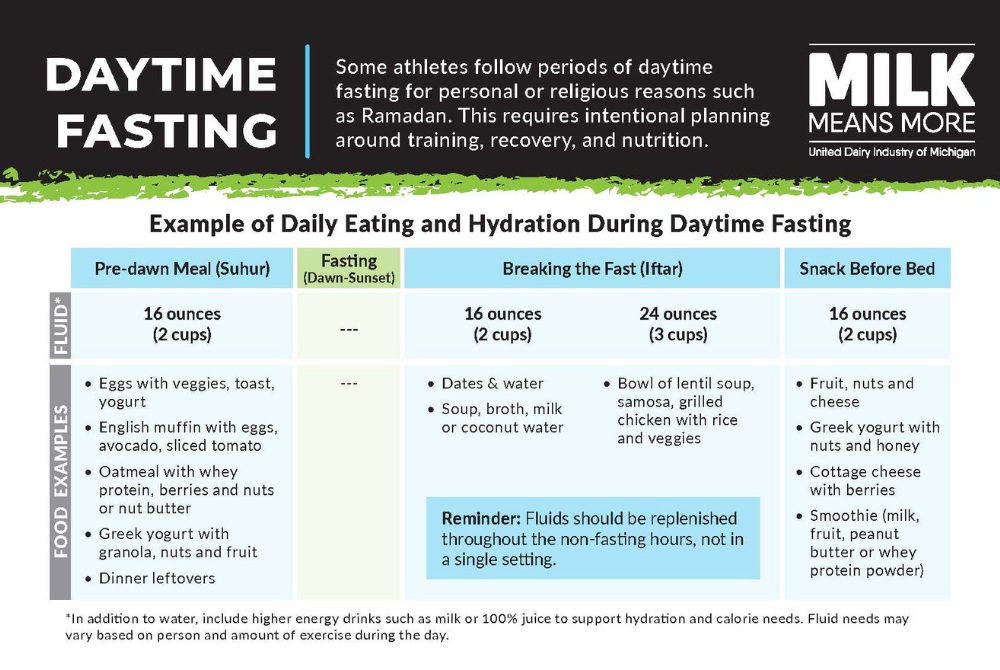
Some athletes follow periods of daytime fasting for personal or religious reasons, such as Ramadan. Fasting from dawn to sunset requires thoughtful planning around nutrition and hydration. With adjustments to meal timing and fluid intake, athletes can continue to support their training, performance, and recovery while observing the fast.
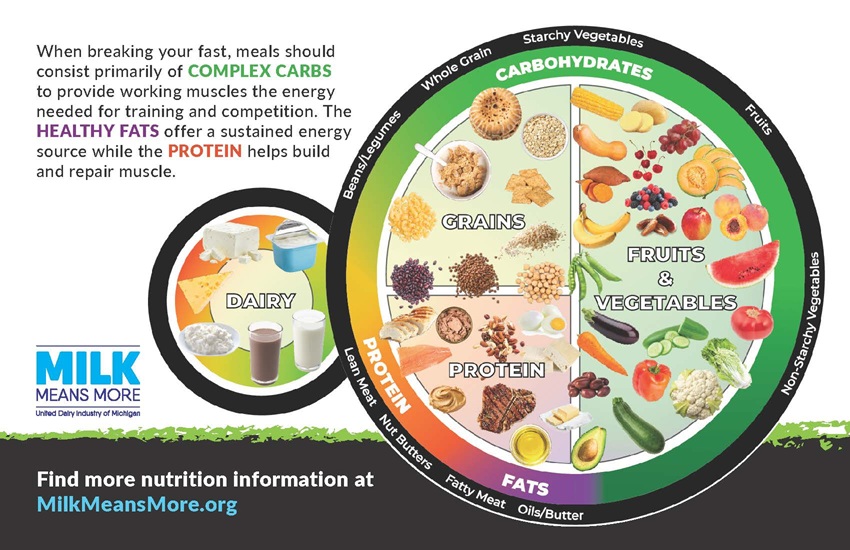
Eating a balanced meal before dawn helps provide sustained energy throughout the day. Including a mix of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats can help fuel muscles and promote fullness.
When breaking fast, athletes should focus on prioritizing complex carbohydrates for energy, along with protein and healthy fats to help the body recover and prepare for the next day’s activity.
Hydration during non-fasting hours is also key, and fluids should be consumed throughout the evening rather than all at once.
With careful planning around meals, fluids, and nutrient balance, athletes can successfully navigate fasting while maintaining strength, endurance, and overall performance.
Click: Practical nutrition & hydration guidance for athletes who observe daytime fasting, such as Ramadan.