Health & Safety: A Look Back, Gallop Ahead
By
John E. (Jack) Roberts
MHSAA Executive Director, 1986-2018
August 7, 2015
We are just completing year six of eight during which we have been addressing the four important health and safety issues that, for ease of conversation, we call the “Four Hs.”
During the 2009-10 and 2010-11 school years, our focus was on Health Histories. We made enhancements in the pre-participation physical examination form, stressing the student’s health history, which we believe was and is the essential first step to participant health and safety.
During the 2011-12 and 2012-13 school years, our focus was on Heads. We were an early adopter of removal-from-play and return-to-play protocols, and our preseason rules/risk management meetings for coaches included information on concussion prevention, recognition and aftercare.
Without leaving that behind, during the 2013-14 and 2014-15 school years, our focus was on Heat – acclimatization. We adopted a policy to manage heat and humidity – it is recommended for regular season and it’s a requirement for MHSAA tournaments. The rules/risk management meetings for coaches during these years focused on heat and humidity management.
At the mid-point of this two-year period, the MHSAA adopted policies to enhance acclimatization at early season practices and to reduce head contact at football practices all season long.
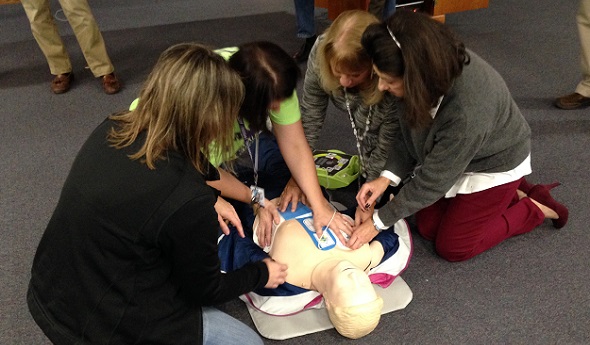
Without leaving any of the three previous health and safety “H’s” behind, during the 2015-16 and 2016-17 school years, our focus will be on Hearts – sudden cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death.
Coinciding with this emphasis is the requirement that all high school level, varsity level head coaches be CPR certified starting this fall. Our emphasis will be on AEDs and emergency action plans – having them and rehearsing them.
On Feb. 10, bills were introduced into both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives, together called the “Safe Play Act (see below),” which addressed three of the four health and safety “H’s” just described: Heat, Hearts and Heads.
For each of these topics, the federal legislation would mandate that the director of the Centers for Disease Control develop educational material and that each state disseminate that material.
For the heat and humidity management topic, the legislation states that schools will be required to adopt policies very much like the “MHSAA Model Policy to Manage Heat and Humidity” which the MHSAA adopted in March of 2013.
For both the heart and heat topics, schools will be required to have and to practice emergency action plans like we have been promoting in the past and distributed to schools this summer.
For the head section, the legislation would amend Title IX of the 1972 Education Amendments and eliminate federal funding to states and schools which fail to educate their constituents or fail to support students who are recovering from concussions. This support would require multi-disciplinary concussion management teams that would include medical personnel, parents and others to provide academic accommodations for students recovering from concussions that are similar to the accommodations that are already required of schools for students with disabilities or handicaps.
This legislation would require return-to-play protocols similar to what we have in Michigan, and the legislation would also require reporting and recordkeeping that is beyond what occurs in most places.
This proposed federal legislation demonstrates two things. First, that we have been on target in Michigan with our four Hs – it’s like they read our playbook of priorities before drafting this federal legislation.
This proposed federal legislation also demonstrates that we still have some work to do.
And what will the following two years – 2017-18 and 2018-19 – bring? Here are some aspirations – some predictions, but not quite promises – of where we will be.
First, we will have circled back to the first “H” – Health Histories – and be well on our way to universal use of paperless pre-participation physical examination forms and records.
Second, we will have made the immediate reporting and permanent recordkeeping of all head injury events routine business in Michigan school sports, for both practices and contests, in all sports and at all levels.
Third, we will have added objectivity and backbone to removal from play decisions for suspected concussions at both practices and events where medical personnel are not present; and we could be a part of pioneering “telemedicine” technology to make trained medical personnel available at every venue for every sport where it is missing today.
Fourth, we will have provided a safety net for families who are unable to afford no-deductible, no exclusion concussion care insurance that insists upon and pays for complete recovery from head injury symptoms before return to activity is permitted.
We should be able to do this, and more, without judicial threat or legislative mandate. We won’t wait for others to set the standards or appropriate the funds, but be there to welcome the requirements and resources when they finally arrive.
Safe Play Act — H.R.829
114th Congress (2015-2016) Introduced in House (02/10/2015)
Supporting Athletes, Families and Educators to Protect the Lives of Athletic Youth Act or the SAFE PLAY Act
Amends the Public Health Service Act to require the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to develop public education and awareness materials and resources concerning cardiac health, including:
- information to increase education and awareness of high risk cardiac conditions and genetic heart rhythm abnormalities that may cause sudden cardiac arrest in children, adolescents, and young adults;
- sudden cardiac arrest and cardiomyopathy risk assessment worksheets to increase awareness of warning signs of, and increase the likelihood of early detection and treatment of, life-threatening cardiac conditions;
- training materials for emergency interventions and use of life-saving emergency equipment; and
- recommendations for how schools, childcare centers, and local youth athletic organizations can develop and implement cardiac emergency response plans.
Requires the CDC to: (1) provide for dissemination of such information to school personnel, coaches, and families; and (2) develop data collection methods to determine the degree to which such persons have an understanding of cardiac issues.
Directs the Department of Health and Human Services to award grants to enable eligible local educational agencies (LEAs) and schools served by such LEAs to purchase AEDs and implement nationally recognized CPR and AED training courses.
Amends the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 to require a state, as a condition of receiving funds under such Act, to certify that it requires: (1) LEAs to implement a standard plan for concussion safety and management for public schools; (2) public schools to post information on the symptoms of, the risks posed by, and the actions a student should take in response to, a concussion; (3) public school personnel who suspect a student has sustained a concussion in a school-sponsored activity to notify the parents and prohibit the student from participating in such activity until they receive a written release from a health care professional; and (4) a public school's concussion management team to ensure that a student who has sustained a concussion is receiving appropriate academic supports.
Directs the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to develop public education and awareness materials and resources to be disseminated to schools regarding risks from exposure to excessive heat and humidity and recommendations for how to avoid heat-related illness. Requires public schools to develop excessive heat action plans for school-sponsored athletic activities.
Requires the CDC to develop guidelines for the development of emergency action plans for youth athletics.
Authorizes the Food and Drug Administration to develop information about the ingredients used in energy drinks and their potential side effects, and recommend guidelines for the safe use of such drinks by youth, for dissemination to public schools.
Requires the CDC to: (1) expand, intensify, and coordinate its activities regarding cardiac conditions, concussions, and heat-related illnesses among youth athletes; and (2) report on fatalities and catastrophic injuries among youths participating in athletic activities.

Permission to Disagree
February 17, 2015

