Using Heads in the Heat of Competition
December 20, 2013
By Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
With so much recent attention to the risks and recognition of concussions in collision sports, athletic leaders have put their heads together to address far more common – but often overlooked – threats to the health of our student-athletes: heat and sudden cardiac arrest.
The No. 1 killer of young athletes is sudden cardiac arrest, while heat stroke victims can surpass that during the year’s hottest months. While the moment of impact leading to a concussion is totally unpredictable, athletic trainers, coaches and administrators have the ability to diminish the occurrences of cardiac arrest and heatstroke. Typically, there is a pre-existing condition, or family history suggesting probabilities for sudden cardiac arrest, which can be treated when detected. And, the perils associated with hot weather – heat stroke, prostration – are almost always completely preventable.
The MHSAA has addressed both issues recently. With assistance from numerous medical governing bodies, the annual pre-participation physical form was revamped and expanded prior to the 2011-12 school year to include comprehensive information regarding participants’ medical history.
In May, the Representative Council adopted a Model Policy for Managing Heat & Humidity (see below), a plan many schools have since adopted at the local level. The plan directs schools to monitor the heat index at an activity site once the air temperature reaches 80 degrees and provides recommendations when the heat index reaches certain levels, including ceasing activities when it rises above 104 degrees.
The topic of heat-related illnesses receives a lot of attention at the start of fall when deaths at the professional, collegiate and interscholastic levels of sport occur, especially since they are preventable in most cases with the proper precautions. In football, data from the National Federation of State High School Associations shows 41 high school players died from heat stroke between 1995 and 2012.
“We know now more than we ever have about when the risk is high and who is most at risk, and we’re now able to communicate that information better than ever before to administrators, coaches, athletes and parents," said Jack Roberts, executive director of the MHSAA. “Heat stroke is almost always preventable, and we encourage everyone to avail themselves of the information on our website.
“Schools need to be vigilant about providing water during practices, making sure that students are partaking of water and educating their teams about the need for good hydration practices.”
All of which is not to say concussions aren’t a serious matter; they are. In fact, leaders in sport safety can take advantage of the concussion spotlight to illuminate these additional health threats.
A recent New York Times story (May 2013) by Bill Pennington featured a February 2013 gathering in Washington organized by the National Athletic Trainers Association. In the article, Dr. Douglas J. Casa, professor of kinesiology at the University of Connecticut and Chief Operating Officer of the Korey Stringer Institute (founded in the late NFL offensive lineman’s name to promote prevention of sudden death in sport), suggests just that.
“All the talk about head injuries can be a gateway for telling people about the other things they need to know about, like cardiac events and heat illness,” said Casa in the article. “It doesn’t really matter how we get through to people as long as we continue to make sports safer.”
Education and prevention methods need to find a permanent place in school programs if those programs are to thrive and avoid becoming targets at which special interest groups can aim budgetary arrows.
Dr. Jonathan Drezner, the president of the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, said in the New York Times piece that sudden cardiac arrest is “so incredibly tragic and stunning that people aren’t comfortable putting it into the everyday conversation. I do wish, to some extent, it was something people talked more about because we are getting to a place where we could prevent many of these deaths.”
When it comes to heat-related deaths or illnesses, the prevention efforts can be even more successful by educating the masses. And, these efforts can be done at minimal cost to schools.
“That’s the thing about curtailing exertional heat illness: it’s 100 percent preventable, and unlike other health threats to athletes, the solutions can be very low-tech and inexpensive,” said Dr. Michael F. Bergeron, the director of the National Institute for Athletic Health & Performance at the University of South Dakota’s Sanford Medical Center, in the New York Times story.
To assist with cost and data maintenance, the MHSAA has teamed with Sports Health to provide schools with psychrometers (heat measurement instruments) at a discounted rate, and has built online tools to track heat and humidity conditions.
Managing heat and humidity policy
- Thirty minutes prior to the start of an activity, and again 60 minutes after the start of that activity, take temperature and humidity readings at the site of the activity. Using a digital sling psychrometer is recommended. Record the readings in writing and maintain the information in files of school administration. Each school is to designate whose duties these are: generally the athletic director, head coach or certified athletic trainer.
- Factor the temperature and humidity into a Heat Index Calculator and Chart to determine the Heat Index. If a digital sling psychrometer is being used, the calculation is automatic.
If the Heat Index is below 95 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Optional water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
If the Heat Index is 95 degrees to 99 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Optional water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
Contact sports and activities with additional equipment:
- Helmets and other possible equipment removed while not involved in contact.
- Reduce time of outside activity. Consider postponing practice to later in the day.
- Recheck temperature and humidity every 30 minutes to monitor for increased Heat Index.
If the Heat Index is above 99 degrees to 104 degrees:
All Sports
- Provide ample amounts of water. This means that water should always be available and athletes should be able to take in as much water as they desire.
- Mandatory water breaks every 30 minutes for 10 minutes in duration.
- Ice-down towels for cooling.
- Watch/monitor athletes carefully for necessary action.
- Alter uniform by removing items if possible.
- Allow for changes to dry T-shirts and shorts.
- Reduce time of outside activity as well as indoor activity if air conditioning is unavailable.
- Postpone practice to later in the day.
Contact sports and activities with additional equipment
- Helmets and other possible equipment removed if not involved in contact or necessary for safety.
- If necessary for safety, suspend activity.
Recheck temperature and humidity every 30 minutes to monitor for increased Heat Index.
If the Heat Index is above 104 degrees:
All sports
- Stop all outside activity in practice and/or play, and stop all inside activity if air conditioning is unavailable.
Note: When the temperature is below 80 degrees there is no combination of heat and humidity that will result in need to curtail activity.
PHOTO: The Shepherd volleyball team includes hydration during a timeout in a match this fall.
And the MHSAA Survey Says ...
April 2, 2015
By Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
A survey of MHSAA member schools was conducted in the fall of 2014 aimed to determine opinions for and against a myriad of out-of-season coaching/contact period topics within the school year.
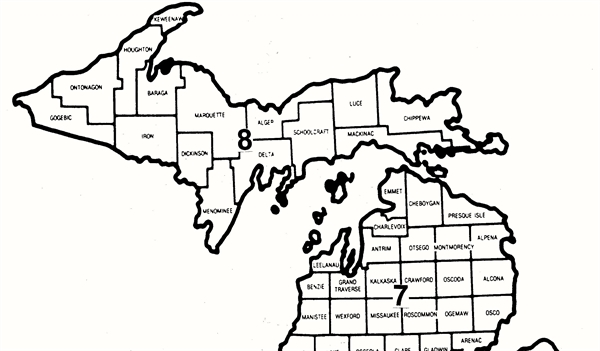
Below are some of the summaries drawn from that survey, plus a map of zones referred to in a number of points.
Survey Summary and Highlights
The larger the school, the higher the percentage of students who are involved in organized non-school sports.
The Detroit metro area (Zone 3) has the highest percentage of respondents in each of two groups in which the highest percentage of students are involved in organized non-school sports ... the 60 to 80% and 40 to 60% groups. The Grand Rapids area (Zone 6) ranks second.
The northern Lower Peninsula (Zone 7) and the Upper Peninsula (Zone 8) have the highest percentage of respondents in the group in which the lowest percentage of students are involved in organized non-school sports . . . the 0 to 20% group. This is also true of Zones 1, 2 and 5, although less dramatically.
In the majority of schools, coaches work with students out of season under the three- or four-player rule for a few weeks just before the season. This is generally true regardless of school classification or geographic zone.
In nearly 80% of schools, the frequency of coaches working with students out of season under the three- or four-player rule is one or two days a week.
100% of schools that sponsor basketball hold open gyms for basketball. Two-thirds of volleyball schools hold volleyball open gyms. Half of lacrosse schools hold lacrosse open gyms. Open gyms in baseball, softball and soccer occur in 40 to 45% of responding schools. Open gyms are less common for other sports.
More than half of all schools conduct open gyms for only a few weeks, just before the season begins.
In 85% of schools, the frequency of open gyms is one or two days a week.
The multi-sport athlete is common in schools of every classification, but more common in Class C and D schools than in Class A and B.
The multi-sport athlete is common in schools of every geographical zone, but more common in Zones 1, 2, 4, 7 and 8 than in Zones 3, 5 and 6.
Two-thirds of schools do not ban athletes from out-of-season workouts while in-season in a different school sport. Permitting weightlifting is most common (84%), then three- or four-player workouts (70%), then conditioning (66%) and open gyms (65%), and finally non-school competitions (57%).
Single-sport coaches are more common in smaller schools than larger (perhaps because fewer sports are sponsored in smaller schools).
For one question, schools were asked to rate ideas from 1 (I like the concept) to 6 (I do not like the concept). Average would be 3.5.
More than 60% of schools favor a no-contact period for all out-of-season sports at the start of every other sport’s season. (Support ranges from 55% for Class A schools to 65% for Class D schools and from 56% for Zones 1 and 3 to 71% for Zone 7.)
More than 72% of schools favor (in conjunction with a no-contact period) a defined contact period out of season. Support ranges from 69% for Class B schools to 76% for Class D schools and from 64% in Zone 6 to 88% in Zone 1.
Two-thirds of schools favor setting a limit on the number of contact days for out-of-season coaching. Support ranges from 63% for Class A schools to 72% for Class C schools and from 50% for Zone 2 to 73% for Zone 1.
More than 68% of schools favor setting a limit on the number of contact days in a week. There’s almost no difference based on school class. Support ranges from 58% in Zone 6 to 76% in Zone 5.
Counting days more than players – that is, allowing practice with any number of students for a defined number of days over a period of time – is favored by more than 72% of schools. Support ranges from 69% for Class D to 76% for Class A and from 59% for Zone 5 to 76.5% for Zone 3.
The least support of any idea surveyed was for allowing scrimmage competition (allowing the coach to coach any number of students from that coach’s school in competition against individuals not enrolled in that school).
More than 62% of schools favor a rule that would allow a school coach to coach a non-school team within a defined contact period; that is, a team with students from the coach’s school (and possibly other schools too), but not supported with school funds, administration, insurance, uniforms, etc. Support ranged from 58% for Class C schools to 68% for Class B schools. Support ranged from 54% for Zone 2 to 69% for Zone 6.
This is the most popular proposal (doesn’t preclude others being approved too): 84% of schools favor removing the phrase “under one roof” from Regulation II, Section 11(H) 2 a (see Tuesday's report). Support ranged from 80% for Class D schools to 86% for Class C schools and from 78% in Zone 2 to 89% for Zone 5.
Removing the portion of Interpretation 237 which prohibits setting up rotations that would allow a coach to work with dozens of players who rotate to his/her direct attention in groups of three or four is favored by 69% of schools, but with a distinct large school vs. small school difference of opinion: Class A (80.5% favorable), Class B (72.9%), Class C (61.3%) and Class D (61.7%).

