
MHSA(Q&)A: Beal City volleyball coach Kelly David
October 6, 2012
By Geoff Kimmerly
Second Half editor
 When people in Michigan’s volleyball community hear the name Kelly David, they might think first of the standout from just a few seasons ago. A four-sport standout for the Aggies, she set the volleyball team into the 2009 Class D Semifinals before going on to play at St. Clair Community College.
When people in Michigan’s volleyball community hear the name Kelly David, they might think first of the standout from just a few seasons ago. A four-sport standout for the Aggies, she set the volleyball team into the 2009 Class D Semifinals before going on to play at St. Clair Community College.
David, 20, graduated from high school a little more than two years ago, but is continuing to have an impact on the volleyball court – although now from the sideline as coach of the No. 3-ranked team in Class D. She took over the Beal City program this fall from her former coach, Randy Gallagher and has the Aggies 26-5-1.
Coaching has come naturally for the former floor leader, who already has gained valuable experiences and knowledge to share with her players. She previously coached at the junior high and club levels, the former for her aunt Sue Frederiksen – who coaches Almont’s varsity and is a member of the Michigan Interscholastic Volleyball Coaches Association Hall of Fame.
David is majoring in elementary education at Central Michigan University and sees teaching and coaching in her future for many years to come.
Why did you decide to become a coach?
I played at St. Clair (Community College) for two years, and my aunt had always been into coaching. I ended up coaching her seventh grade volleyball team for two years, and I coached in the Skippers AAU program over there. I found out I liked coaching more than playing.
How have you approached coaching a team that includes players who were freshmen when you were a senior in high school?
Going into it, I knew I wasn’t their friend; I was their coach. I wasn’t close to any of the girls except my sister (Monica, a senior). The people who coached me or were my teachers, (who said) go to class, do this, and you knew they received ultimate respect. I had helped out in previous years, and I knew what I had to do to gain that respect. And (my players) have listened to me.
Did you anticipate questions about you taking over the program only a few years out of high school?
I knew in my head, but I didn’t think it would be a problem in people’s minds. "She’s young, her sister is on the team;" that’s the stuff people might second guess. But I knew how to control the team, and having my sister on it wasn’t a big teal. So far (issues) haven’t happened. I’ve coached teams in previous years, and I’d always been the leader when I did play. I think that helps.
What were your goals coming into the season?
I had a lot of goals. Obviously, I wanted us to go far, like in the past. The biggest thing I noticed playing college from high school, the players knew the game of volleyball. They were smart. They had the same athletic ability as those I played against in high school, but they were just smarter. Knowing how to position the ball on the court, knowing the game, and I wanted to teach (my players) the game of volleyball. It’s important to know the game, and then we can work around the obstacles.
What did you learn by watching your aunt coach?
Just how strong you have to be. When I watch her coach, she’s very enthusiastic. But when someone does something wrong, she lets them know. That’s an important thing.
When did you first know you were interested in coaching?
When I was in high school, when I played, I’d help the other players. I noticed that was something I liked to do. I’d watch someone and pick up things they could fix. I thought about it in high school, and once I actually did it with the seventh graders, it wasn’t a job for me. It’s fun. Coaching is something I want to do. They want to be playing volleyball – that’s why they’re on the team. Everyone wants to be there, and we’re trying to accomplish the same thing.
What has been the biggest challenge during your first season?
The biggest challenge is handling the pressure. I know the team can do well. We’re ranked third in the state right now. But it’s getting them to perform the way they can perform, getting them to come together at the right time.
I’d also like to mention that Beal City (already) had a great program, from (former coaches) Randy Gallagher and before I came, Kelly Knuth. I’m just happy to step in and try to continue what they did.
PHOTO: Beal City huddles during a break in its match against Shepherd this season. (Click to see more from HighSchoolSportsScene.com).
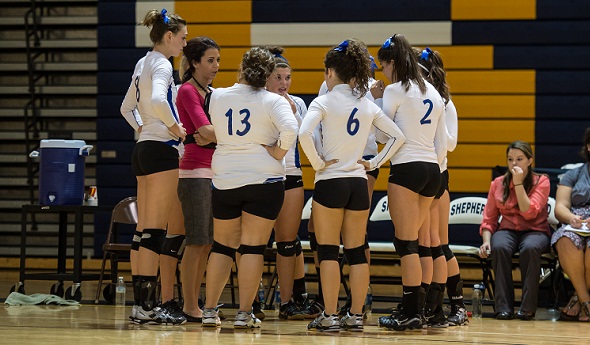

'Anyone Can Save a Life' Aims to Prepare
July 28, 2015
By Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
It was 2008 when Jody Redman and staff at the Minnesota State High School League developed an emergency action plan to provide guidance and procedure in the event of sudden cardiac arrest during scholastic athletic competition.
The desired response from schools upon receipt of the plan was, well, less than enthusiastic.
“Only about 40 percent of our schools used the information and implemented the program,” said Redman, associate director for the MSHSL. “Our focus was completely on sudden cardiac arrest, that being the worst-case scenario regarding athletic-related health issues.”
The MSHSL asked the University of Minnesota to survey its member schools, and results showed that the majority of schools not on board simply felt a sudden cardiac arrest “would never happen at their school.” Naive or not on the schools’ parts, that was the reality – so Redman went back to revise the playbook.
“We expanded the plan to deal with all emergencies, rather than specific incidents,” Redman said. “Now it’s evolved so that we are prepared to deal with a variety of situations which put participants at risk. We shifted gears and got more schools to participate.”
Did they ever. And not just in Minnesota.
This summer, the “Anyone Can Save a Life” program, authored by the MSHSL and the Medtronic Foundation, is being disseminated to high schools nationwide with the financial support of the NFHS Foundation. The program will reach schools in time for the 2015-16 school year.
Once received, schools will find that there are two options for implementation, via in-person training or online.
“The in-person method is facilitated by the athletic administrator with the assistance of a training DVD” Redman said. “The important element is the follow through, ensuring coaches return their completed Emergency Action Plan (EAP). With the e-learning module on anyonecansavealife.org, individuals will complete an e-learning module that will walk them through the details of their specific plan, and as they answer questions, the information will automatically generate a PDF of the Emergency Action Plan (EAP) which they can edit at a later date as information changes.”
Schools will find five major components of the program to be received this summer: the first is an implementation checklist for the AD, explaining their role. Next are sections for in-person training, online training and event staff training. The last item contains a variety of resources that will ensure the successful implementation of a comprehensive emergency response to all emergencies.
Generally speaking, the program prompts schools to assemble preparedness teams, broken into four categories: a 911 team, a CPR team, an AED team and a HEAT STROKE team. The groups are made up of coaches and their students who will be in close proximity to all after-school activities.
“The reality about school sports is, at 3:30 every day the office closes and any type of medical support ceases to exist,” Redman said. “We then send thousands of students out to gyms, courts, fields and rinks to participate without systemic support for emergencies. This program puts into place that systemic support.”
Another stark reality is that the majority of schools in any state do not have full-time athletic trainers. Even for those fortunate enough to employ such personnel, it’s most likely the training “staff” consists of one person. That one body can only be in one place at one time, and on widespread school campuses the time it takes to get from one venue to another could be the difference between life and death.
“Athletic trainers can champion the program, but someone needs to oversee that every coach has a completed EAP in place,” Redman said. “For every minute that goes by when a cardiac arrest occurs, chance for survival decreases by 10 percent.”
Thus, it’s imperative to train and grant responsibility to as many people as possible, including student-athletes. In fact, students are a vital component to having a successful EAP. Students will be put in position to call 911, to meet the ambulance at a pre-determined access point, to locate the nearest AED, to make sure emersion tubs are filled for hot-weather practices, and for those who are trained, to assist with CPR. Coaches will identify students at the beginning of the season and prior to an emergency taking place. They will provide them with the details of the job they are assigned so they will be ready to assist in the event of an emergency.
“We have game plans for every sport, and for every opponent on our schedule,” Redman said. “But we don’t have a plan to save the life of a member of our team or someone attending a game at our school.
“This is about developing a quick and coordinated response to every emergency so we give someone in trouble a chance at survival, and then practicing it once or twice a season. We have ‘drop the dummy’ drills where we drop a dummy and evaluate how it went, and how everyone performed. In one scenario, it’s the coach that goes down, and then you have a group of 15- or 16-year-olds standing there. That’s why students have to take ownership of this, too.”
The key to an effective emergency action plan is to utilize and empower students in every sport and at every level to be a part of the response team. Following are brief descriptions of the teams.
The 911 Team
- Two students will call 911 from a pre-determined phone and provide the dispatcher with the location and details of the emergency.
- Two students will meet the ambulance at a pre-determined access point and take them to the victim.
- Two students will call the athletic trainer, if one is available, and the athletic administrator and alert them to the emergency.
The CPR Team
- The coach is the lead responder on this team and is responsible for attending to the victim and administering CPR, if necessary, until trained medical personnel arrive.
- One person is capable of providing effective CPR for approximately two minutes before the quality begins to diminish. Having several students trained and ready to administer CPR will save lives.
The AED Team
- Two students will retrieve the AED and take it to the victim.
- Two students will physically locate the athletic trainer, if one is available, and take him or her to the victim.
The Heat Stroke Team
- Two students identify locations of emersion tub, water source, ice source and ice towels.
- Two students prepare tub daily for practices and events.
For more information, visit anyonecansavealife.org or contact the MSHSL.

