Health & Safety: A Look Back, Gallop Ahead
By
John E. (Jack) Roberts
MHSAA Executive Director, 1986-2018
August 7, 2015
We are just completing year six of eight during which we have been addressing the four important health and safety issues that, for ease of conversation, we call the “Four Hs.”
During the 2009-10 and 2010-11 school years, our focus was on Health Histories. We made enhancements in the pre-participation physical examination form, stressing the student’s health history, which we believe was and is the essential first step to participant health and safety.
During the 2011-12 and 2012-13 school years, our focus was on Heads. We were an early adopter of removal-from-play and return-to-play protocols, and our preseason rules/risk management meetings for coaches included information on concussion prevention, recognition and aftercare.
Without leaving that behind, during the 2013-14 and 2014-15 school years, our focus was on Heat – acclimatization. We adopted a policy to manage heat and humidity – it is recommended for regular season and it’s a requirement for MHSAA tournaments. The rules/risk management meetings for coaches during these years focused on heat and humidity management.
At the mid-point of this two-year period, the MHSAA adopted policies to enhance acclimatization at early season practices and to reduce head contact at football practices all season long.
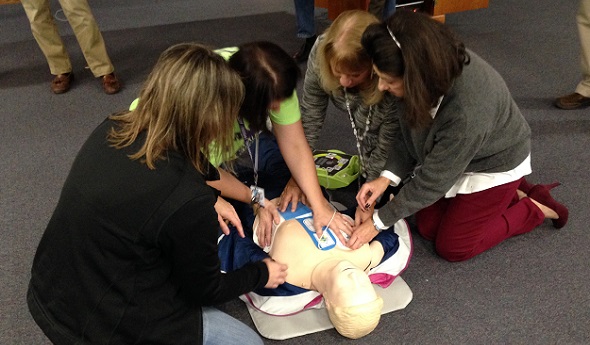
Without leaving any of the three previous health and safety “H’s” behind, during the 2015-16 and 2016-17 school years, our focus will be on Hearts – sudden cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death.
Coinciding with this emphasis is the requirement that all high school level, varsity level head coaches be CPR certified starting this fall. Our emphasis will be on AEDs and emergency action plans – having them and rehearsing them.
On Feb. 10, bills were introduced into both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives, together called the “Safe Play Act (see below),” which addressed three of the four health and safety “H’s” just described: Heat, Hearts and Heads.
For each of these topics, the federal legislation would mandate that the director of the Centers for Disease Control develop educational material and that each state disseminate that material.
For the heat and humidity management topic, the legislation states that schools will be required to adopt policies very much like the “MHSAA Model Policy to Manage Heat and Humidity” which the MHSAA adopted in March of 2013.
For both the heart and heat topics, schools will be required to have and to practice emergency action plans like we have been promoting in the past and distributed to schools this summer.
For the head section, the legislation would amend Title IX of the 1972 Education Amendments and eliminate federal funding to states and schools which fail to educate their constituents or fail to support students who are recovering from concussions. This support would require multi-disciplinary concussion management teams that would include medical personnel, parents and others to provide academic accommodations for students recovering from concussions that are similar to the accommodations that are already required of schools for students with disabilities or handicaps.
This legislation would require return-to-play protocols similar to what we have in Michigan, and the legislation would also require reporting and recordkeeping that is beyond what occurs in most places.
This proposed federal legislation demonstrates two things. First, that we have been on target in Michigan with our four Hs – it’s like they read our playbook of priorities before drafting this federal legislation.
This proposed federal legislation also demonstrates that we still have some work to do.
And what will the following two years – 2017-18 and 2018-19 – bring? Here are some aspirations – some predictions, but not quite promises – of where we will be.
First, we will have circled back to the first “H” – Health Histories – and be well on our way to universal use of paperless pre-participation physical examination forms and records.
Second, we will have made the immediate reporting and permanent recordkeeping of all head injury events routine business in Michigan school sports, for both practices and contests, in all sports and at all levels.
Third, we will have added objectivity and backbone to removal from play decisions for suspected concussions at both practices and events where medical personnel are not present; and we could be a part of pioneering “telemedicine” technology to make trained medical personnel available at every venue for every sport where it is missing today.
Fourth, we will have provided a safety net for families who are unable to afford no-deductible, no exclusion concussion care insurance that insists upon and pays for complete recovery from head injury symptoms before return to activity is permitted.
We should be able to do this, and more, without judicial threat or legislative mandate. We won’t wait for others to set the standards or appropriate the funds, but be there to welcome the requirements and resources when they finally arrive.
Safe Play Act — H.R.829
114th Congress (2015-2016) Introduced in House (02/10/2015)
Supporting Athletes, Families and Educators to Protect the Lives of Athletic Youth Act or the SAFE PLAY Act
Amends the Public Health Service Act to require the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to develop public education and awareness materials and resources concerning cardiac health, including:
- information to increase education and awareness of high risk cardiac conditions and genetic heart rhythm abnormalities that may cause sudden cardiac arrest in children, adolescents, and young adults;
- sudden cardiac arrest and cardiomyopathy risk assessment worksheets to increase awareness of warning signs of, and increase the likelihood of early detection and treatment of, life-threatening cardiac conditions;
- training materials for emergency interventions and use of life-saving emergency equipment; and
- recommendations for how schools, childcare centers, and local youth athletic organizations can develop and implement cardiac emergency response plans.
Requires the CDC to: (1) provide for dissemination of such information to school personnel, coaches, and families; and (2) develop data collection methods to determine the degree to which such persons have an understanding of cardiac issues.
Directs the Department of Health and Human Services to award grants to enable eligible local educational agencies (LEAs) and schools served by such LEAs to purchase AEDs and implement nationally recognized CPR and AED training courses.
Amends the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 to require a state, as a condition of receiving funds under such Act, to certify that it requires: (1) LEAs to implement a standard plan for concussion safety and management for public schools; (2) public schools to post information on the symptoms of, the risks posed by, and the actions a student should take in response to, a concussion; (3) public school personnel who suspect a student has sustained a concussion in a school-sponsored activity to notify the parents and prohibit the student from participating in such activity until they receive a written release from a health care professional; and (4) a public school's concussion management team to ensure that a student who has sustained a concussion is receiving appropriate academic supports.
Directs the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration to develop public education and awareness materials and resources to be disseminated to schools regarding risks from exposure to excessive heat and humidity and recommendations for how to avoid heat-related illness. Requires public schools to develop excessive heat action plans for school-sponsored athletic activities.
Requires the CDC to develop guidelines for the development of emergency action plans for youth athletics.
Authorizes the Food and Drug Administration to develop information about the ingredients used in energy drinks and their potential side effects, and recommend guidelines for the safe use of such drinks by youth, for dissemination to public schools.
Requires the CDC to: (1) expand, intensify, and coordinate its activities regarding cardiac conditions, concussions, and heat-related illnesses among youth athletes; and (2) report on fatalities and catastrophic injuries among youths participating in athletic activities.

Taking a Healthy Approach to Sports
By
Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
November 8, 2013
During election years, it’s a familiar rallying cry: “Four more years! Four more years!”
It’s become commonplace following the third quarter of football games around the country for members of the leading team to march down the gridiron with four fingers raised on one outstretched hand as teams switch ends of the field to signify, “Fourth quarter is ours; finish the job.”
The number four also is significant in education with school terms identified as freshman, sophomore, junior and senior years.
To that end, the MHSAA is imploring everyone involved in educational athletics to go back to school in 2013-14 with a four-year mission in mind: “Four Thrusts for Four Years.”
The goal is to attain and maintain advanced degrees in sports safety, positioning Michigan schools in the center of best practices for ensuring the health of our product and students, today and beyond.
“Just a brief look around all levels of today’s athletic landscape reveals heightened awareness of health and safety issues,” said MHSAA Executive Director Jack Roberts. “Interscholastic sports as a whole – and particularly school sports in Michigan – has long led the charge to employ the safest contest rules and provide the healthiest environments for our games and participants.
“But, to put it in athletic terms, we can’t sit on the lead,” Roberts added. “We can, and must, improve our games in order to guarantee their existence for future generations. That is our goal, our thrust in the coming years.”
Following are the focal points for this four-year plan:
- Implement heat and humidity management policies at all schools for all sports.
- Require more initial and ongoing sports safety training for more coaches.
- Revise practice policies generally, but especially for early in the fall season.
- Modify game rules to reduce the frequency of the most dangerous play situations, and to reduce head trauma.
The directive actually kicked off last March, when the Representative Council approved a heat management policy for MHSAA tournaments and a detailed model policy for schools. While not setting requirements for member schools during the regular season, it suggests actions based on heat index – the degree of felt discomfort derived by combining temperature and humidity measurements – that are designed to minimize the risk of heat-related illness during interscholastic participation.
The policy is mandatory for all MHSAA tournaments beginning this school year, and the MHSAA plans to monitor schools’ adoption of the plan throughout the year to determine best policies moving forward.
Laminated cards containing the policy and heat index chart were printed and mailed to schools in June and continue to be disseminated at statewide meetings this fall. Two publications, Heat Ways and Safety Blitz, were published, mailed and posted to MHSAA.com, heightening awareness of healthy practice regimens, and schools have been offered discounted psychrometer prices through the MHSAA to assist in their efforts to properly monitor weather conditions.
“This action was significant; but it’s just the next step in a continuous series of actions being taken to make school sports as healthy as possible for students,” said Roberts.
The MHSAA’s proactive movements toward a safer tomorrow are taking place concurrently, rather than sequentially. While the heat and humidity plan is the most developed of the four “thrusts,” other initiatives are underway. Today’s climate prompts such action.
From the NCAA’s new “targeting fouls” to the NFL’s “crown” rule, and of course Major League Baseball’s Biogenesis/PED debacle, the headlines off the field in August centered on protecting the games rather than simply playing them. Like it or not, it’s the type of news fans need to get used to as their favorite sports audible to option plays in order to steer clear of the endangered species list.
The situation can’t be overstated. Athletics at all levels has been approaching a crossroads for years, and the time to heed the signals has come.
“Let’s make one thing abundantly clear: The people in charge of football at all levels are wise to craft rules that make the game safer, even if those rules will be controversial,” wrote Andy Staples for SI.com College Football on July 23.
The story continued: “As more information arrives about the long-term dangers of the headshots football players absorb at the high school, college and pro levels, something has to change. The next few years will be messy. The game needs saving, because if it continues as it has, it will get decimated by lawsuits and by parents of young children who decide the potential adverse effects aren't worth the risk.”
When kids stop playing, numbers at the high school level and beyond are bound to diminish as well. To trumpet the vast benefits of interscholastic football while easing parents’ minds on safety concerns, the MHSAA formed a Football Task Force in the spring of 2013. The task force is the first of several to be convened during the next four school years, and the objectives of each are to promote the sports involved as safe, low-risk, competitive athletics through the development of better practice policies and modification of playing rules.
“These task forces will be central to the overarching mission of preserving sports for years to come,” said Roberts. “We believe the MHSAA Football Task Force has set a foundation on which to build. Our discussions involving revised practice policies have reached the draft stage, and we intend to have formal proposals ready to present to the Representative Council in March 2014.”
The work of the 13-member task force – made up of football coaches and school administrators from around the state – will be reviewed by the Michigan High School Football Coaches Association, the MHSAA Football Committee and at the MHSAA League Leadership meeting for fine-tuning prior to reaching the Council.
“It is important that we provide opportunities for children to participate in interscholastic athletics and crucial that we do all we can to ensure they will be safe when they do,” said Football Task Force member Tammy Jackson, principal at East Jordan High School, who has a sports medicine background. “The MHSAA has taken an active role in promoting safety by convening the Task Force to examine current rules and consider modifications to further protect children.”
With so much publicity concerning football safety, the football group was a natural to become the first of several task forces to be assembled.
“We must educate the public on the benefits of all school sports,” said task force member Bill Chilman, superintendent of Beal City Schools. “In the case of football, it must be impressed upon people that it is statistically a very safe game when taught and played properly. The Football Task Force being proactive rather than reactive to this safety movement is key to promoting the lifelong values of football and all school sports.”
And within that public is a group which has the most vested concerns: the parents.
“There is more information available to the general public regarding sport and sport injuries, and unfortunately parents and kids all too often hear about the negative side of sport,” suggests Mike Bakker, athletic director at Fenton High School, and another member of the MHSAA Football Task Force. “It is imperative for the integrity of the sport of football to have coaches and administrators provide information about the safety of the game and the steps we take to keep kids safe. We must educate parents about the proper way to play the game and the signs to look for if problems arise.”
Without getting into the minutia of the new NCAA and NFL playing rules regarding use of the helmet, suffice it to say this will be an interesting fall during which to monitor penalties and their effects on injury numbers, particularly when it comes to concussions.
The rules changes have been reported and debated at the national level ad nauseam, and the mood seems to inexplicably tilt toward skepticism and criticism from the very group that would stage a revolt of epic proportions if football ever became extinct: the fans.
Case in point: six targeting fouls were called in 75 games during the opening weekend of college football over Labor Day Weekend (one ejection was overturned by replay), and the outcry began. Analysts and fans are afforded frame-by-frame replays which onfield officials do not have the luxury of seeing before throwing the flag.
Like it or not, the rules are in place. And, they have been implemented to protect the future of the game. The impetus now falls to the caretakers of the game – the officials – who no doubt will bear the brunt of disapproving masses in the stadiums. Yet, football is their livelihood too; both players and officials are expected to make adjustments.
At Officiate Michigan Day and the ensuing National Association of Sports Officials Summit this past July in Grand Rapids, the theme was clear: “The game has changed, and the officiating has to change with it.”
From NFL Referee Jeff Triplette to SEC Coordinator of Officials Scott Shaw to Big Ten Referee Alex Kemp and Fox Sports NFL Rules Analyst Mike Pereira – people who have been around the block – the message delivered was that the changes are necessary for the health and growth of football.
“We’re talking about taking out a specific type of play that, quite honestly, you didn’t see that much of before about 10 years ago,” Triplette said during a player safety panel at the NASO Summit. “They still played defense, there were still great hits. But somehow, these violent types of tackles began to get notoriety – whether it was all the ESPN highlights, YouTube, and maybe a combination of all of that stuff – and players started to celebrate those hits, and that became the goal.”
Not only can the game become safer; it might even become better by going retro. In recent comments on The Sports XChange, NFL analyst and former coach John Madden said, “You are always concerned how any change will impact the game. In this case, players are not going for the head shot, that big hit. They are keeping their heads up. Better tackling has become the unintended consequence. That's a good thing. Good for football. Good for kids watching. Players are tackling the way they are supposed to, with their shoulders and wrapping up. The big hit, the big replay had become so popular that tackling suffered.”
In high school, the most notable rule change involving helmets involves penalties for players who lose their helmets during a play. However, illegal helmet contact continues to be a point of emphasis and carries a minimum of a 15-yeard penalty as it has for many years. In the NCAA the mantra on helmet-to-helmet blows is, “When in doubt throw them out,” as the foul now carries with it a player ejection.
That is not the high school rule—yet—but officials at all levels need to be on the lookout. Kemp was quick to warn a roomful of prep football officials during Officiate Michigan Day, “We’ve been told to err on the side of safety, and these plays will result in ejection,” while also adding that such plays will be reviewed by replay officials. “That portion of the rule isn’t there in high school yet, but be ready for it; it’s coming, so when it happens in your games take notice and determine the severity.”
Which brings us to contest rules for safer play. During the next few years, various sport groups will be assembled to follow the MHSAA football task force’s lead in scrutinizing rules and developing proposals for revisions or additions to be submitted to the National Federation of State High School Associations. Initial football discussions receiving some traction involve changing the enforcement spot on post-interception penalties and limiting the number of yards teams can run up on free kicks. Before any submissions are made to the NFHS Football Committee, the task force will conduct research and present findings to Michigan committees.
“We can make changes ourselves – through MHSAA sport committees – for the subvarsity level, but our committees can only make recommendations to national rules committees for varsity level play,” explained Roberts. “Over the next four years, we will be asking our sport committees to give more time to the most dangerous plays in their sport – identifying what they are and proposing how to reduce that danger.”
While the football task force here at home is finalizing practice policy proposals targeted for implementation in the fall of 2014, Texas and Illinois are two states which launched restrictions with the opening of football this season. Spokespersons from both states indicate that coaches and school administrators have been pleased with the new formats.
Coaches no doubt will need to adjust practice itineraries and budget time wisely. Administrators need to remind staffs that the new era is dawning in the name of player safety, which is paramount to all parties.
“In game situations, coaches want our officials to throw the flag on late hits, low hits and other illegal contact,” Roberts said. “These are incidents that they have no control over. They do have control over practice time and teaching fundamentals; so let’s encourage safety measures that we can control, and employ those tactics to help the game prosper.”
Education will key the efforts to align coaches of all sports – and all levels – in the movement toward a healthy future. School will be in session during the next four years as the MHSAA implements effective and practical means for raising coaches’ preparedness. Three avenues are on the map:
First, the Representative Council mandated that beginning with the 2014-15 school year, all assistant and subvarsity coaches at the high school level must complete the same MHSAA rules meetings currently only required of varsity head coaches or, alternatively, one of the free online sports safety courses posted on or linked from the MHSAA Website that is designated as fulfilling this requirement.
Second, it is proposed that by 2015-16, MHSAA member high schools will be required to certify that all of their varsity head coaches have a valid CPR certification.
Third, it is proposed that by 2016-17, any person who is hired for the first time to be the varsity head coach of a high school team, to begin after July 31, 2016, must have completed either Level 1 or Level 2 of the MHSAA Coaches Advancement Program. The MHSAA is preparing to subsidize some of the course cost for every coach who completes Level 1 or 2.
Together, these changes will move Michigan from one of the states of fewest coaching requirements to a position consistent with the “best practices” for minimizing risk in school sports and providing students a healthy experience.
At stake in these four thrusts – whether for an administrator, coach, official, student-athlete, parent or fan – are the environments that offer so many lessons and the games for which we root.

