Is Baseline Concussion Testing Right For You?
November 2, 2021
Did you know there’s a test that can aid your recovery if you sustain a concussion?
Read on to get the facts about baseline testing from Michelle Gambino-Gorney, a certified athletic trainer for Henry Ford Health System.
What Is Baseline Concussion Testing?
“Baseline testing is an evaluation of your normal brain function that tests for neurocognitive abnormalities,” explains Gambino-Gorney. “We recommend baseline testing prior to the start of a sports season, before tryouts or practice.”
During baseline concussion testing, athletic trainers or physicians collect extensive information about an athlete’s brain health. They evaluate health, family history and neurocognitive function. Gambino-Gorney says that might include assessing everything from balance and reflexes to memory, vision and concentration. “If the athlete does sustain a concussion during the season, we can compare pre-injury test results to post-injury test results and find out how the injury is affecting an athlete’s brain. It helps us make the right recovery plan and determine when it’s safe for them to return to their sport.”
Myth: Concussion Baseline Testing Is Only for Football Players
While baseline testing is ideal for athletes (ages 9 and up) who play high-impact collision sports, any athlete at risk of a concussion should consider baseline testing. This includes football, lacrosse and hockey players, in addition to gymnasts, snowboarders, skateboarders and lots of other athletes.
In fact, even if you just take the occasional weekend bike ride, go jogging or lift weights, there’s no harm in having baseline test results on file. Pre-concussion screenings can also benefit people with physically demanding jobs, such as first responders, military personnel and tactical athletes.
Myth: You Only Need to Get Baseline Testing Once
Just as your joints and muscles change as you get older, your brain changes, too. It’s best to get annual baseline testing. Yearly tests help your healthcare team keep track of your brain health over time. They can spot problems or changes early, before they develop into serious issues. Ask your physician about baseline neurocognitive testing as part of your annual sports physical.
Myth: Baseline Testing Is Only Useful If You Get a Concussion
First and foremost, baseline testing tracks your physical and mental well-being. Even if you never sustain a concussion, the test is a way to stay proactive about your brain health. Gambino-Gorney explains that they can look at test results across seasons to detect changes in neurocognitive function that can indicate disorders such as:
► Anxiety
► Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
► Depression
► Learning disabilities
Myth: Baseline Testing Diagnoses a Concussion
Baseline testing is not a diagnostic tool for concussions. It’s one piece of all the information a healthcare provider needs to determine if you sustained a mild traumatic brain injury. In addition to comprehensive neurocognitive testing, your provider assesses a broad range of concussion signs and symptoms to confirm a diagnosis after you’ve sustained an impact to your head.
To find a primary care or sports medicine specialist at Henry Ford, visit henryford.com or call 1-800-436-7936.
Michelle Gambino-Gorney is a certified athletic trainer in the Henry Ford Kutcher Clinic for Concussion and Sports Neurology.
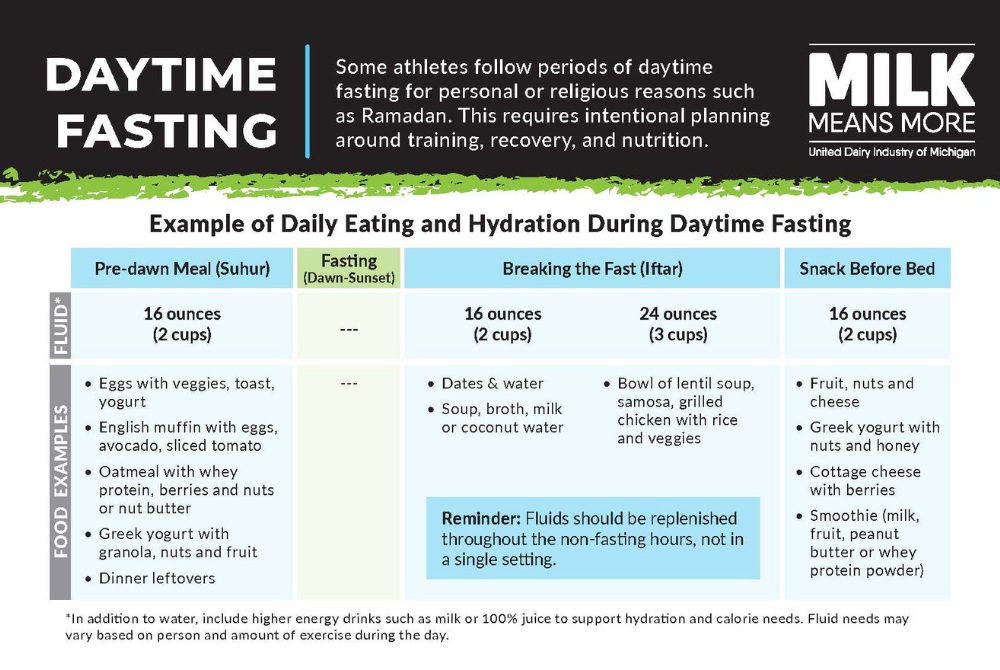
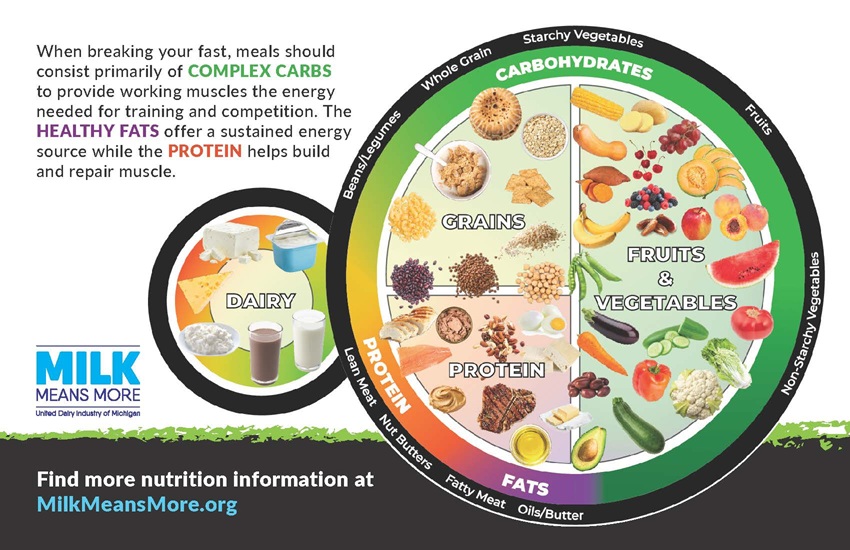
Fuel Up for Daytime Fasting with Proper Nutrition, Hydration
February 17, 2026
Some athletes follow periods of daytime fasting for personal or religious reasons, such as Ramadan. Fasting from dawn to sunset requires thoughtful planning around nutrition and hydration. With adjustments to meal timing and fluid intake, athletes can continue to support their training, performance, and recovery while observing the fast.
Eating a balanced meal before dawn helps provide sustained energy throughout the day. Including a mix of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats can help fuel muscles and promote fullness.
When breaking fast, athletes should focus on prioritizing complex carbohydrates for energy, along with protein and healthy fats to help the body recover and prepare for the next day’s activity.
Hydration during non-fasting hours is also key, and fluids should be consumed throughout the evening rather than all at once.
With careful planning around meals, fluids, and nutrient balance, athletes can successfully navigate fasting while maintaining strength, endurance, and overall performance.
Click: Practical nutrition & hydration guidance for athletes who observe daytime fasting, such as Ramadan.