How Can COVID-19 Impact Student-Athletes' Return-To-Play?
October 5, 2021
COVID-19 And Student Athletes: How Can the Virus Impact Return-To-Play?
The end of summer marked the start of the school year, and for student athletes, the kickoff of the fall sports season. For many, COVID-19 sidelined practices, team gatherings and games to some extent last year. And while there is still hope that young athletes will have more opportunity to play this season despite rising cases of the Delta variant, there are other factors causing concern among athletes and their parents.
According to Ramsey Shehab, M.D., a sports medicine physician for Henry Ford Health System, many athletes are concerned about reaching peak performance after a long time off or after they have recovered from a COVID diagnosis. He reassures students that the feeling of exhaustion or even underperformance compared to past years is to be expected when you take time off or after fighting an illness.
“When you are infected with a virus, it taxes your immune system, and all of your energy goes towards fighting off that infection,” says Dr. Shehab. “You’ll likely feel weak and more tired during this time.”
Fortunately, as the body begins to recover, you’ll start to feel more like yourself again as you get your energy back. But this doesn’t mean that you won’t lose some of that fitness and endurance you’ve built up.
“It only takes about a week of deconditioning to set you back from peak athletic abilities,” says Dr. Shehab. “It is completely expected that your body will need time to get back to performing at your best.”
Playing Sports After Recovering From COVID-19
The unfortunate news: COVID-19 affects people differently in the long term. Some people are able to recover and get back to their routine without delay, whereas others see further complications months after an infection.
Akshay Khandelwal, M.D., a cardiologist with Henry Ford Health System, breaks down some of the more serious findings regarding COVID-19 and your heart health.
“With COVID-19, there is a risk of direct injury like heart failure or an arrhythmia due to the stress your body is under while fighting off the virus,” says Dr. Khandelwal. “As a result, having the virus can cause inflammation of the heart, a condition called myocarditis.”
Because of this, talking to your doctor before returning to a sport is a must if you had COVID or are recovering from the virus. It is important to make sure there are no systemic changes to your body such as overall heart health and lung function. They will be able to rule out any long-term effects that could impact your fitness output.
Expert-Recommended Steps for Return-To-Play
As you get back to your game, both experts share their insights for a healthy recovery:
1. Take quarantine periods seriously. If you are sick, even if you don’t necessarily feel sick, make sure you are taking time to rest and recover properly. “Don’t try to push or overexert yourself,” says Dr. Khandelwal. “It could prolong your recovery.”
2. Get back to training slowly. “Start using low-exertion activities to get your body used to working out again,” says Dr. Shehab. “Once you are able to handle each activity, you can push ahead to something more challenging.” Realistically, it may take a couple of weeks before you are able to get back to your peak.
3. Listen to your body. If workouts seem increasingly difficult, talk with your doctor or trainer before pushing yourself further. You can also help your body recover by making healthy, thoughtful choices:
► Get plenty of sleep
► Warm up and cool down before and after workouts
► Stay hydrated
► Take breaks when you’re tired
► Practice injury prevention
► Make smart food choices
4. Get vaccinated. If medical or religious reasons, or age requirements aren’t stopping you from getting the vaccine, consider getting the shot for yourself and those around you. The Delta variant is highly transmittable, meaning that, it is much easier for it to spread to teammates and family members than the original strain of the virus. To learn more about the COVID-19 vaccine, visit our Vaccine FAQs page.
Talk to your doctor to learn more about safely returning to a sport. To find a doctor, visit henryford.com or call 1-800-436-7936.
Dr. Ramsey Shehab is the deputy chief of Sports Medicine at Henry Ford Health System. He sees patients at the Henry Ford Center for Athletic Medicine and Henry Ford Medical Center - Bloomfield Township.
Dr. Akshay Khandelwal is an interventional cardiologist who sees patients at Henry Ford Medical Center – Second Avenue.
Fuel Up for Daytime Fasting with Proper Nutrition, Hydration
February 17, 2026
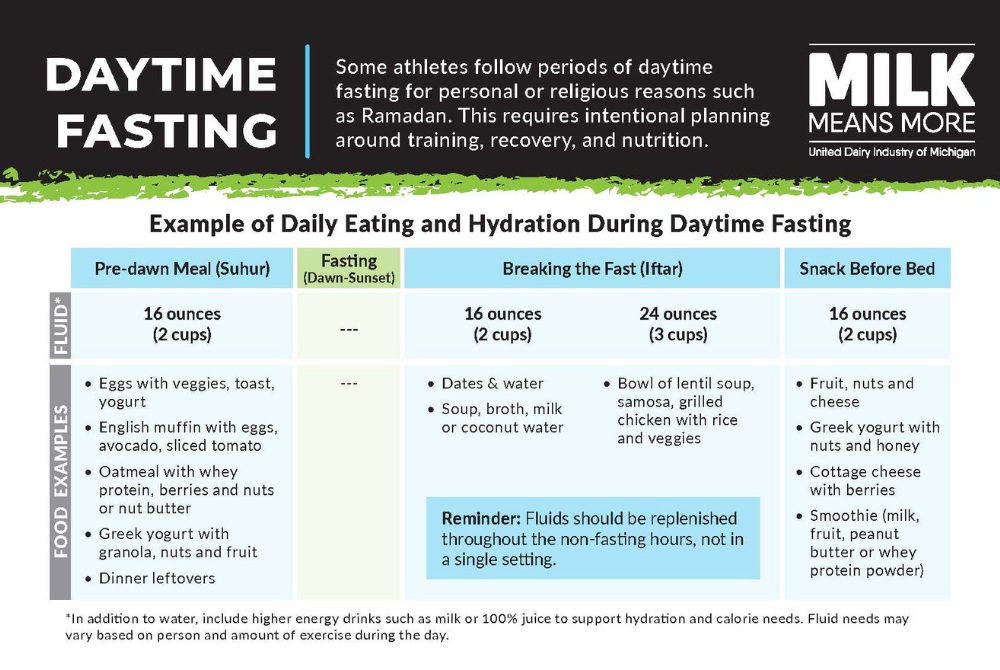
Some athletes follow periods of daytime fasting for personal or religious reasons, such as Ramadan. Fasting from dawn to sunset requires thoughtful planning around nutrition and hydration. With adjustments to meal timing and fluid intake, athletes can continue to support their training, performance, and recovery while observing the fast.
Eating a balanced meal before dawn helps provide sustained energy throughout the day. Including a mix of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats can help fuel muscles and promote fullness.
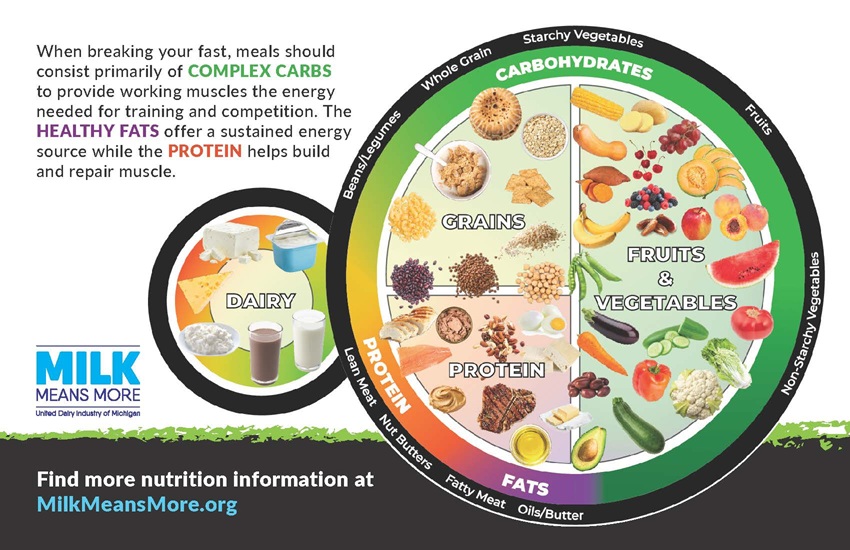
When breaking fast, athletes should focus on prioritizing complex carbohydrates for energy, along with protein and healthy fats to help the body recover and prepare for the next day’s activity.
Hydration during non-fasting hours is also key, and fluids should be consumed throughout the evening rather than all at once.
With careful planning around meals, fluids, and nutrient balance, athletes can successfully navigate fasting while maintaining strength, endurance, and overall performance.
Click: Practical nutrition & hydration guidance for athletes who observe daytime fasting, such as Ramadan.